
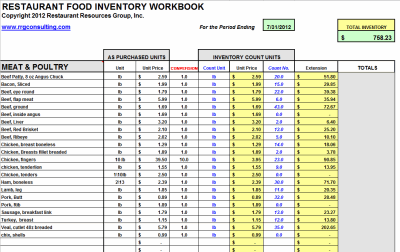
Daily Usage) = Safety Stock Number Reorder Point Formula The difference between the two is your safety stock number. Then multiply the average lead time (in days) with the average historic daily usage rate. Multiply the maximum number of days it will take to stock the item (lead time) and the maximum historic sales rate per day (daily usage). To determine an item’s safety stock number: The perfect balance between understocking and overstocking is called your safety stock number or “par level.” It’s important to determine how much stock you should always have on hand to meet demand-without needlessly wasting money by overstocking. No business wants to lose sales due to running out of an item. Here are four fundamental formulae you should know. If you are math-shy, don’t worry some can be calculated for you by inventory management software. There are a variety of calculations you can do to make stock management easier. When you spot a slow-selling item, it might be time to have a sale or promotion to liquidate it. This can be an important retail inventory management practice for businesses that need to keep on top of trends petering out or seasons changing, for example in apparel businesses.
Since excess stock is a waste of space and capital, spend some time identifying stock that hasn’t sold in six to twelve months. But sometimes there are factors to consider beyond your historical sales.
It can, for example, pinpoint the number of sales a product had during the same week of the previous year.
How to do inventory for small business software#
Software can take you far when it comes to forecasting. This is called “cycle counting.” Having robust technology and inventory software in place that assists with inventory control can significantly reduce the time you spend on counting stock. Some businesses choose to spread stock reconciliation out over the year by choosing a product class to audit each month or each quarter. Some small businesses do this annually, but depending on your industry, you may want to count stock more frequently. Periodic AuditingĮvery business needs to schedule inventory counting sessions from time to time.
But it can also be important for businesses that stock other products that are at risk of becoming obsolete over time. The FIFO method is crucial for businesses that deal in perishable goods like food or flowers. FIFO: First In, First OutįIFO is a common-sense approach requiring that the first items received are the first items sold. For that reason, it is important to set your safety stock levels using the formula given in the next section. You wouldn’t want to streamline your stock so much that you are in danger of selling out, leaving you with dissatisfied customers. Not only does JIT reduce the amount of stock that has to be tracked and insured, but it also reduces waste and the likelihood that excess products will need to be liquidated.Īdhering to the JIT methodology too aggressively does carry an element of risk. The Just-in-Time Method (JIT) is a planning strategy that aims to minimize stock levels. Here are five key strategies: Just-In-Time Method Successful small business owners tend to employ a variety of tried-and-true methodologies for streamlining their stock ordering processes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
